27/10/2022 - Dupont analysis
cfa | dupont analysis
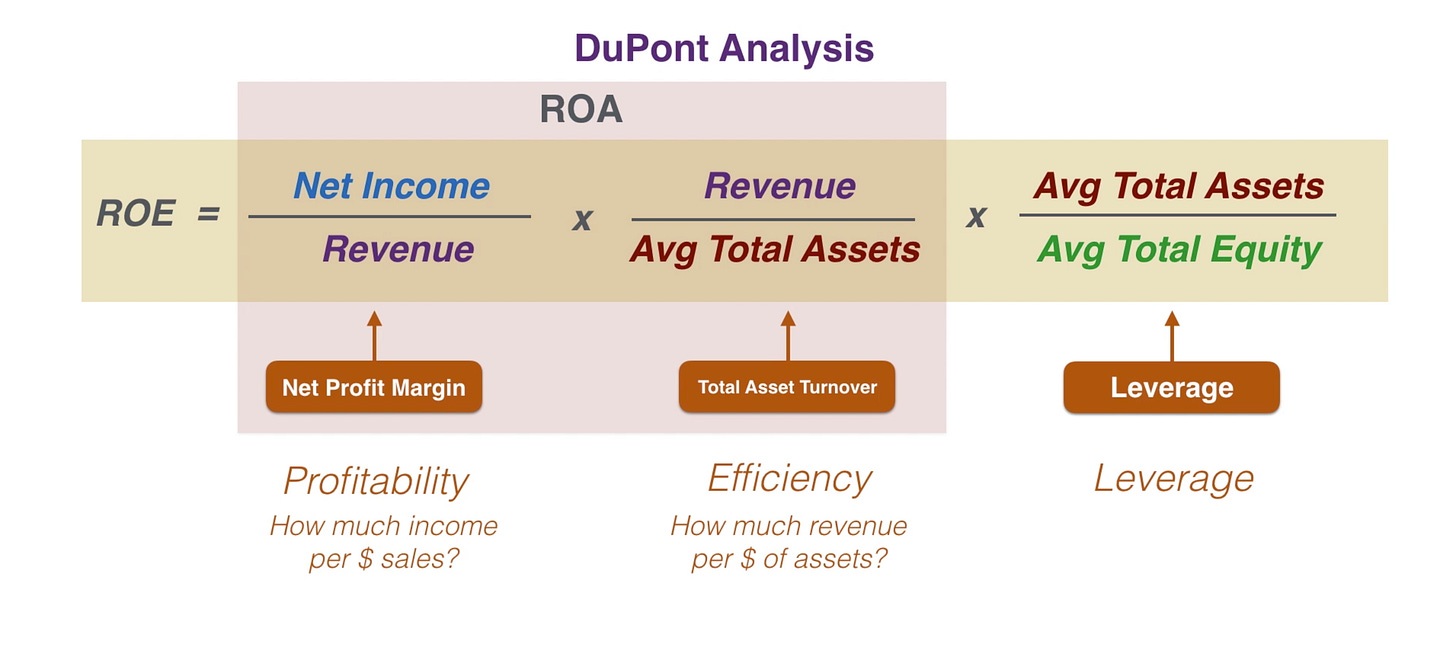
Dupont analysis breaks down the ROE (return on equity) to mini elements to examine which one is affecting the company’s performance.
It could not be concluded that a company’s underperforming just because its ROE is declining over the years.
ROE giảm có thể đến từ nguyên nhân mở rộng sản xuất, doanh thu giảm do chi phí và vốn đầu tư lớn và tài sản, nhưng tốc độ tăng trưởng qua các năm sau khi các nhà máy đi vào hoạt động sẽ là dấu hiệu cho sự tăng trở lại của chỉ số ROE.
Cũng có trường hợp ROE tăng dần đều, và mức chênh lệch không đáng kể. > > Công ty đang có cải thiện một cách đều đặn qua từng năm.
Ghi chú:
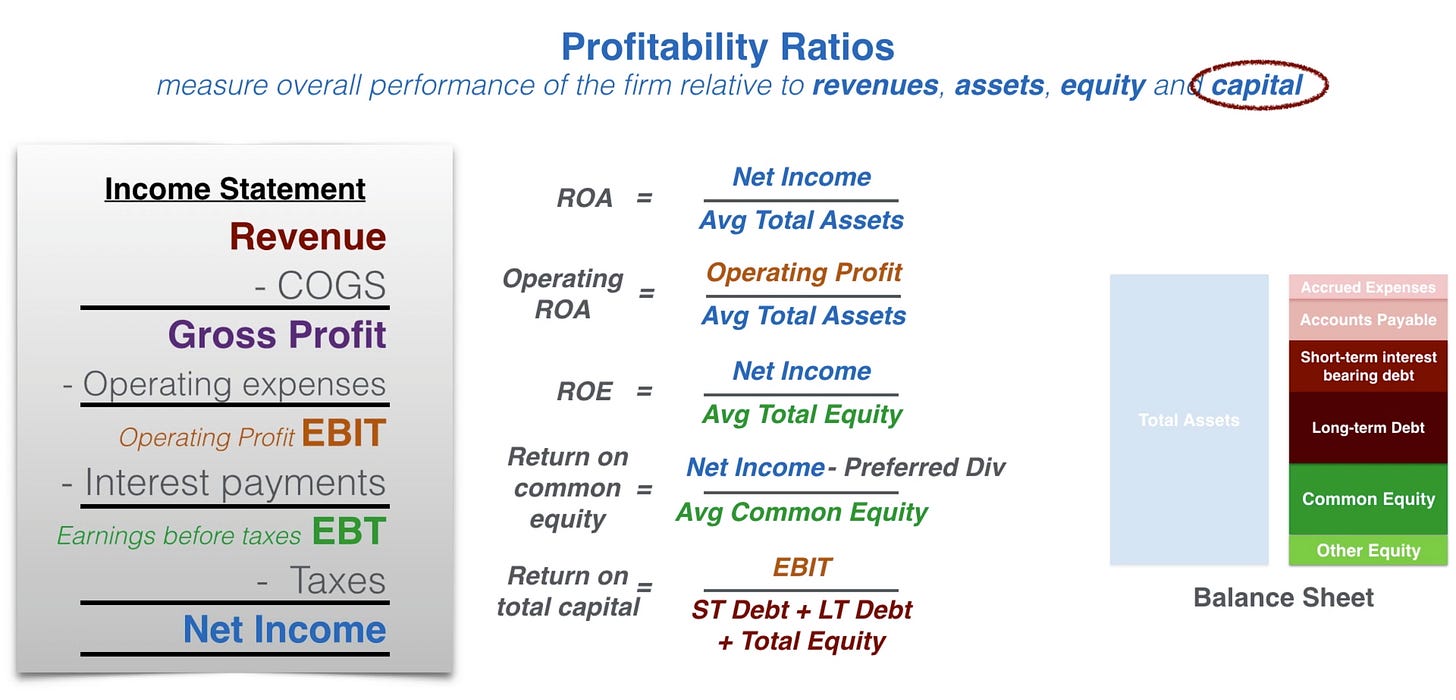
EBT: earning before tax
EBIT: earning before interest
Leverage = avg total asset/ avg total equity
ROE = ROA x leverage
ROA = (net income/revenue x revenue/total assets)
Muốn tăng EBIT margin (biên lợi nhuận trước lãi vay hay operating income), thì cần giảm chi phí (COGS) > tăng revenue
The company can use leverage (borrowing more money) to boost ROE instead of managing cost
Asset turnover ratio
The asset turnover ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate revenue. Imagine a company had $100 of assets, and it made $1,000 of total revenue last year. The assets generated 10 times their value in total revenue, which is the same as the asset turnover ratio and can be calculated as follows:
A normal asset turnover ratio will vary from one industry group to another. For example, a discount retailer or grocery store will generate a lot of revenue from its assets with a small margin, which will make the asset turnover ratio very large. On the other hand, a utility company owns very expensive fixed assets relative to its revenue, which will result in an asset turnover ratio that is much lower than that of a retail firm.3